Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch is a distributed, RESTful search and analytics engine designed for fast and scalable data retrieval.
ingestr supports Elasticsearch as both a source and destination.
URI format
The URI format for Elasticsearch is as follows:
elasticsearch://username:password@host:port?secure=<secure>&verify_certs=<verify_certs>URI parameters:
username: The username used to authenticate with Elasticsearch (optional).password: The password associated with the specified username (optional).host: The host address of the Elasticsearch server.port: The port number used by the Elasticsearch server (default: 9200).secure: Enables HTTPS when set to true. By default, it is true. Set to false for HTTP connections.verify_certs: Verifies TLS certificates when set to true. By default, it is true. Only used for sources.
The same URI structure can be used both for sources and destinations.
Using Elasticsearch as a source
Source Table
<index-name>: Fetches all available documents from the specified index.
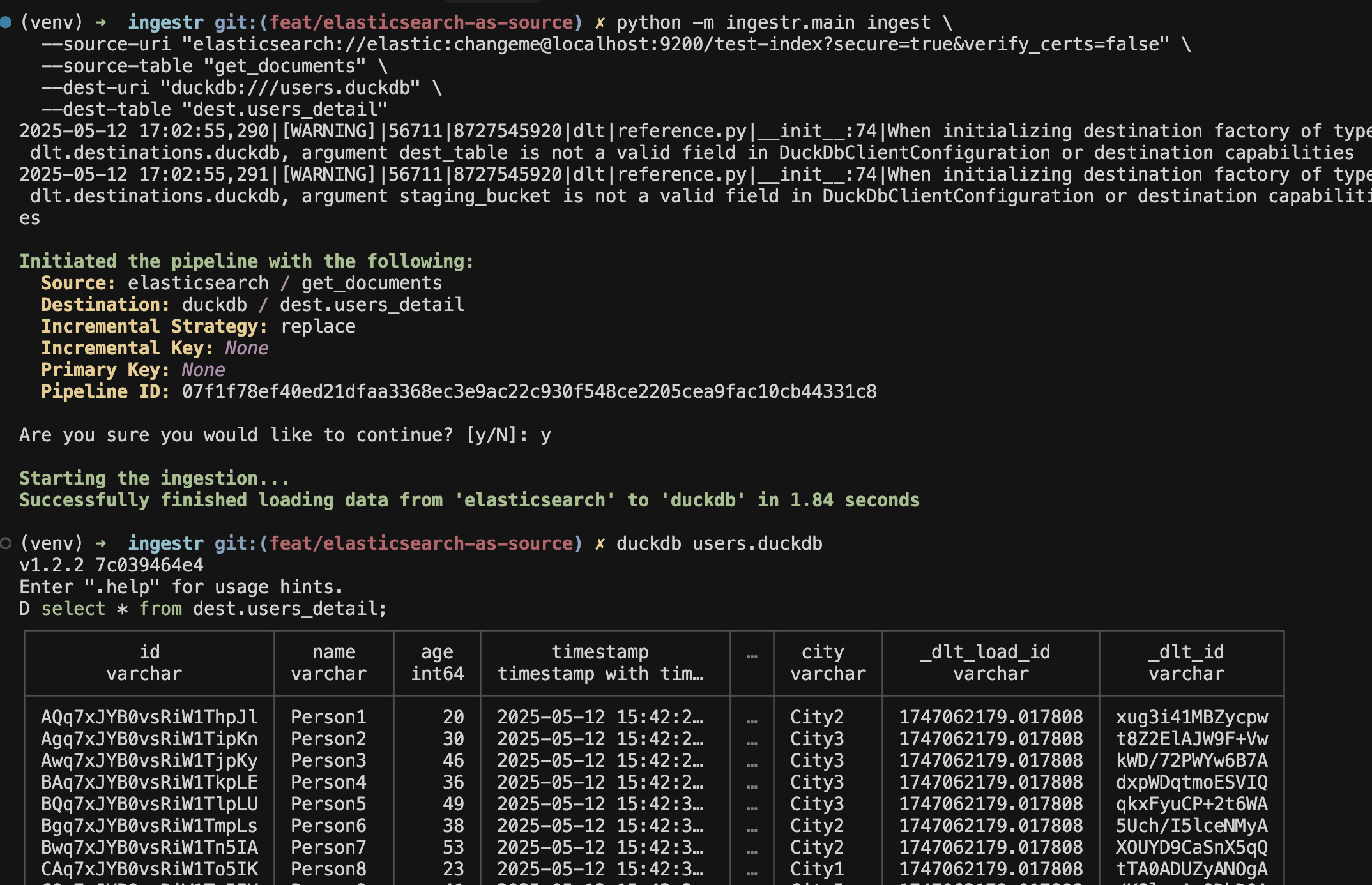
ingestr ingest \
--source-uri "elasticsearch://elastic:changeme@localhost:9200?secure=false&verify_certs=false" \
--source-table 'test-index' \
--dest-uri "duckdb:///users.duckdb" \
--dest-table 'dest.users_detail'This command retrieves all documents from the test-index in Elasticsearch and copy them to the dest.users_detail table in DuckDB.
Using Elasticsearch as a destination
Elasticsearch can be used as a destination to load data from various sources. The --dest-table option specifies the index name where data will be loaded.
Elasticsearch Cloud (with authentication)
ingestr ingest \
--source-uri "postgres://user:pass@localhost:5432/mydb" \
--source-table "public.users" \
--dest-uri "elasticsearch://username:password@cluster.cloud.es.io:443" \
--dest-table "users_index"NOTE
Cloud Elasticsearch instances typically use HTTPS (port 443). The secure parameter defaults to true, so HTTPS is used automatically.
Local Elasticsearch with authentication
ingestr ingest \
--source-uri "csv:///path/to/data.csv" \
--source-table "data" \
--dest-uri "elasticsearch://elastic:changeme@localhost:9200?secure=false" \
--dest-table "myindex"Local Elasticsearch without authentication
ingestr ingest \
--source-uri "csv:///path/to/data.csv" \
--source-table "data" \
--dest-uri "elasticsearch://localhost:9200?secure=false" \
--dest-table "myindex"TIP
By default, ingestr uses a "replace" strategy which deletes the existing index before loading new data. The target index will be created automatically if it doesn't exist.